Changes in technology have completely revolutionised the way people drive; cars are now safer, smoother and more efficient than ever before, with intelligent features that were not so very long ago the stuff of sci-fi movies.
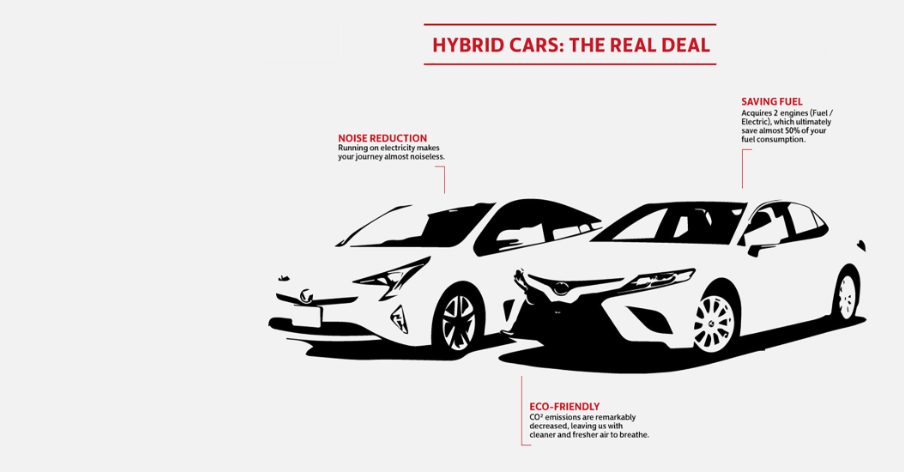
The Hybrid Electrical Vehicle (HEV) is one of the most exciting developments in motoring. Its benefits vary between being highly economical, more environmentally friendly and even safer than conventional vehicles.
Toyota has always been at the forefront of motoring innovation, and as the creators of the first ever mass-produced hybrid electrical vehicle, we’ve played an important role in helping to protect the planet too. With global CO2 emissions a major concern for all governments, vehicles that don’t guzzle gallons of gas have become increasingly popular over recent years. Advances in battery technology have been a major factor in altering opinions, with today’s versions offering greater fuel efficiency, control and added luggage space.
The Batteries
Toyota HEVs have two batteries; one is a standard battery for the high voltage system and the other an auxiliary with a 12V capacity that supplies power to the hybrid system.
These are comprised of one nickel-metal hydride and one lithium-ion battery. Both are able to charge at constant levels by using regenerative braking and surplus power; making the new HEV battery both powerful and reliable.
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density (the amount of energy that can be stored per unit of weight or volume). Nickel-metal hydride batteries are stable even at low temperatures. The newly created electrode material found in nickel-metal hydride batteries dramatically increase battery power and charge performance, while lithium-ion batteries offer a huge improvement in output performance thanks to their reduced cell resistance.
Toyota HEVs, equipped with THS (Toyota Hybrid System), combine the advantages of gasoline engines and electric motors, giving drivers the best of both worlds. While car buyers traditionally had to choose between efficiency and performance, HEV vehicles offer a new synergy between motor and engine that even cynics can appreciate. Maximum torque is delivered from the moment of acceleration without affecting consumption, conserving fuel without sacrificing performance.
The main electrolyte in the HEV battery is a potassium chloride solution that is stored in the safest part of the car (usually the trunk). Anyone concerned about the danger of electric shock doesn’t need to worry. In the unlikely event that the vehicle should end up under water, the high voltage system is automatically shut down, giving its passengers the safety measures they not only demand, but deserve.
The battery operates at a 30% to 80% State of Charge (SOC) to minimise stress, applying short power bursts for acceleration. Under normal use, HEV batteries consume less than 2% of their total capacity per mile, making for a highly efficient vehicle with no need to warm up the engine on a cold morning. Furthermore, the electromagnetic waves generated by an HEV battery are no higher than those produced by a standard kitchen appliance.
The future, today
Moving forward, Toyota is conducting research into next-generation batteries with an energy density that greatly exceeds that of the current models. The company is creating new systems and methods to promote the wider use of Hybrid Electric Vehicles and have recently introduced wireless charging, which enables batteries to be charged without connecting any cables. Plans are also underway to improve fuel efficiency by a further 10% by developing and introducing SIC power semiconductors, which in turn will significantly reduce power loss issues.
Through a combination of research, dedication and expert craftsmanship, Toyota is committed to making HEVs the standard on roads across the globe. The future for the HEV is bright, and Toyota is leading the way.